ApoB is a better predictor of heart disease risk than a traditional cholesterol test. Unlike LDL cholesterol, which measures the mass of cholesterol in particles, ApoB counts the actual number of atherogenic particles that can penetrate artery walls and cause plaque buildup.
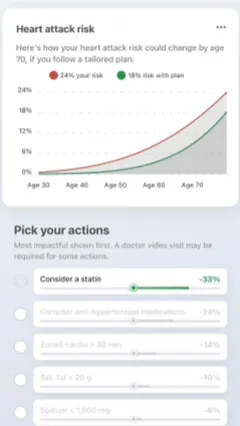 Building a plan to reduce your heart disease risk. Source: Empirical Health app
Building a plan to reduce your heart disease risk. Source: Empirical Health app
While dramatic reductions in ApoB typically take several weeks to months, you can immediately start building evidence-based habits that will lower your ApoB levels over time. In this article, we’ll cover the 18 most effective lifestyle interventions to lower ApoB backed by clinical research.
Evidence-based lifestyle changes to reduce your ApoB levels
The major levers that drive ApoB levels are nutrition, exercise, smoking, sleep, stress, and body weight. Each of these can reduce ApoB by anywhere from 3-8%.
We’ll start with nutrition.
How to lower ApoB through diet and supplements
The most important nutritional interventions to lower ApoB are increasing fiber, adding plant sterols, and reducing saturated fat. The following table summarizes key dietary interventions and their effects on ApoB (or LDL cholesterol, when ApoB data wasn’t available):
| Intervention | Study Design | Participants | ApoB/LDL Change | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduce saturated fat by 1% of calories | Meta-analysis of 60 trials | 1,600+ participants | 1.9 mg/dL LDL | Mensink et al., 2003 |
| Add 10g soluble fiber daily | Meta-analysis of 67 RCTs | 2,990 participants | 7.8 mg/dL LDL | Brown et al., 1999 |
| Plant sterol supplements (2g/day) (‡) | Meta-analysis of 41 trials | 3,800+ participants | 6-12% LDL | Ras et al., 2023 |
| Unfiltered coffee consumption (3-5 cups/day) | Meta-analysis of 12 studies | 1,017 participants | +5.4 mg/dL LDL* | Cai et al., 2012 |
| Replace refined grains with whole grains | RCT | 316 participants | -5.1% ApoB | Tighe et al., 2010 |
| Omega-3 supplements (1-4g/day) | Meta-analysis of 26 RCTs | 1,400+ participants | -3.6% ApoB | Leslie et al., 2015 |
(‡) The effect of plant sterols on cardiovascular disease (as opposed to just cholesterol) is more complex — some research suggests people with mutations in the ABCG5/8 genes should be cautious.
Fiber supplements, such as psyilum husk, are an easy win. When getting fiber through diet, it’s important to focus on soluble fiber. For example a cup of kale has 7g fiber—but 70% is insoluble. In contrast, an apple has 6g of fiber, 74% of which is soluble.
Plant sterol supplements are recommended by the National Lipid Association to lower ApoB. A common plant sterol supplement is red yeast rice. There’s no benefit to more than 2g / day of plant sterols, so there’s no need to overdo this one.
Finally, reducing saturated fat does have an effect on ApoB for most people. While this is often the most difficult dietary change to make, since many foods with saturated fat are delicious, it can be very influential.
A surprising, and easy, swap is to replace unfiltered coffee (French press, espresso) with filtered coffee. Unfiltered coffee contains cafestol and kahweol, which raise ApoB and LDL. Replacing refined grains with whole grains, and omega-3 supplementation (or getting omega-3 through diet), are also quite helpful.
How to lower ApoB through exercise
Workouts that lower ApoB are broadly similar to workouts that improve VO2Max. High intensity interval training shows the strongest individual effect (albeit in a small trial).
| Intervention | Study Design | Participants | ApoB/LDL Change | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic exercise (150 min/week) | Meta-analysis of 13 RCTs | 1,067 participants | -5% ApoB | Kelley et al., 2004 |
| High-intensity interval training | RCT | 81 participants | -15% ApoB | Tjønna et al., 2008 |
| Resistance training (3x/week) | Meta-analysis of 29 trials | 1,329 participants | -6.2 mg/dL LDL | Kelley & Kelley, 2009 |
| Combined aerobic + resistance | RCT | 196 participants | -8.2% ApoB | Sigal et al., 2007 |
Other lifestyle changes that lower ApoB and LDL
Most of us know we should lose weight, stop smoking, reduce stress, and get adequate sleep. So it’s not surprising that each of these has been shown in the medical literature to reduce ApoB:
| Intervention | Study Design | Participants | ApoB/LDL Change | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss (5-10% body weight) | Meta-analysis of 70 trials | 10,000+ participants | -8.9% ApoB | Dattilo & Kris-Etherton, 1992 |
| Smoking cessation | Longitudinal study | 1,566 participants | +13% HDL, -5% LDL | Gepner et al., 2011 |
| Stress reduction (meditation) | RCT | 201 participants | -9.6 mg/dL LDL | Schneider et al., 2012 |
| Adequate sleep (7-8 hours) | Cross-sectional study | 1,666 participants | Lower ApoB in adequate sleepers | Kaneita et al., 2008 |
ApoB-lowering drugs
If lifestyle changes are a screwdriver, medications are a power drill. Common and cheap medications like statins can lower ApoB by 24-45%. Nwer medications like PCSK9 inhibitors can lower ApoB by 50-60% on top of the effect of statins.
Here’s a summary of the major medications used to lower ApoB, their effect size, and mechanism:
| Medication Class | Example Drugs | Typical ApoB Reduction | Mechanism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statins | Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin | 25-45% | HMG-CoA reductase inhibition | First-line therapy |
| Ezetimibe | Zetia | 15-20% | Cholesterol absorption inhibition | Often combined with statins |
| PCSK9 inhibitors | Evolocumab, Alirocumab | 50-60% | Increases LDL receptor recycling | Injectable, expensive |
| Bempedoic acid | Nexletol | 15-25% | ATP citrate lyase inhibition | Used in combination with statins |
Percentage reductions are approximate. They’ll vary based on baseline levels, dosing, and individual response.
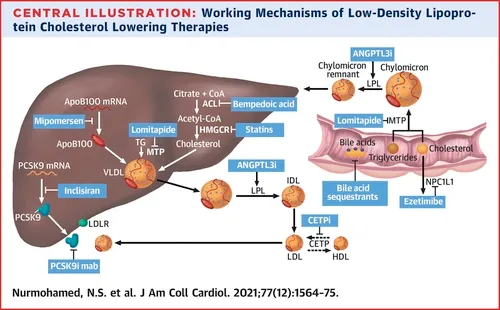 Different medications use different mechanisms to lower ApoB and LDL (Source).
Different medications use different mechanisms to lower ApoB and LDL (Source).
Each class of medications relies on a different mechanism to lower ApoB. Statins work by blocking HMG-CoA reductase, forcing your liver to produce less cholesterol and pull more cholesterol from your blood. Ezetimibe blocks cholesterol absorption in your small intestine, preventing dietary and biliary cholesterol from entering your bloodstream. PCSK9 inhibitors prevent the degradation of LDL receptors, allowing your liver to clear more ApoB particles from circulation. Bempedoic acid inhibits ATP citrate lyase, providing an alternative mechanism to statins for reducing cholesterol production.
When to consider medication to lower ApoB
ApoB responds to lifestyle changes within 6-12 weeks, though maximum benefits may take 3-6 months. We recommend retesting ApoB after 12 weeks of consistent lifestyle modifications.
Consider medication if ApoB remains >120 mg/dL despite lifestyle changes, you have existing cardiovascular disease (target ApoB <80 mg/dL), or you have diabetes or multiple risk factors (target ApoB <100 mg/dL). An Empirical Health doctor can help you discuss medication options.
How to put your ApoB-lowering plan into action
In this article, we’ve covered 18 ways to reduce ApoB. That’s an awful lot to track. The Empirical Health app for Apple Watch and WearOS/Fitbit can help you build customized plan to lower your ApoB using nutrition, exercise, and medication (Empirical Health doctors write prescriptions in most US states). Give it a try, and let us know what you think.
 Empirical Health app for heart health
Empirical Health app for heart health
ApoB is one of the strongest predictors of future heart attacks and strokes. Every reduction in ApoB translates to meaningful cardiovascular risk reduction. For personalized guidance and ApoB tracking, Empirical Health is here for you.
Get your free 30-day heart health guide
Evidence-based steps to optimize your heart health.
